Red Stealer — Threat Intelligence Walkthrough
Analyze a suspicious executable using VirusTotal and MalwareBazaar to extract IOCs, identify C2 infrastructure, MITRE ATT&CK techniques, and privilege escalation mechanisms.
Overview
| Platform | CyberDefenders |
| Category | Threat Intelligence |
| Difficulty | Easy |
| Focus | IOC Extraction · C2 Identification · MITRE ATT&CK Mapping · Malware Classification |
| Lab Link | Red Stealer |
You are part of the Threat Intelligence team in the SOC. An executable file has been discovered on a colleague’s computer, suspected to be linked to a Command and Control (C2) server, indicating a potential malware infection.
Your task is to investigate this executable by analyzing its hash. The goal is to gather and analyze data beneficial to other SOC members, including the Incident Response team, to respond to this suspicious behavior efficiently.
Objective
The goal of this investigation is to:
- Classify the malware and identify its family
- Extract network-based IOCs (IPs, domains, ports)
- Map behaviors to MITRE ATT&CK techniques
- Identify detection signatures (YARA rules)
- Understand privilege escalation mechanisms
By the end, we will provide actionable intelligence for:
- Firewall block rules
- EDR detection signatures
- Threat hunting queries
- Incident response procedures
Tools Used
Throughout this analysis, the following tools are used:
- VirusTotal — Malware analysis and threat intelligence
- MalwareBazaar — Malware sample database
- ThreatFox — IOC database by abuse.ch
- Whois — Domain registration lookup
Initial Analysis
Sample Hash (SHA256):
1
248fcc901aff4e4b4c48c91e4d78a939bf681c9a1bc24addc3551b32768f907b
We begin our investigation by searching this hash on VirusTotal.
Q1 — Malware Category
Question
Categorizing malware enables a quicker and clearer understanding of its unique behaviors and attack vectors. What category has Microsoft identified for that malware in VirusTotal?
Analysis
Navigate to VirusTotal and search for the sample hash. Go to the Detection tab and review the security vendors’ analysis.
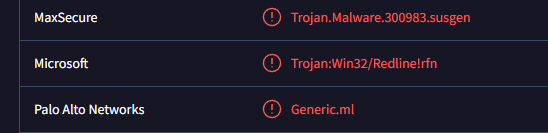 Microsoft identifies this malware as Trojan:Win32/Redline!rfn
Microsoft identifies this malware as Trojan:Win32/Redline!rfn
Looking through the security vendors’ detections, Microsoft identifies this malware as:
1
Trojan:Win32/Redline!rfn
The malware category is:
1
Trojan
This classification aligns with RedLine Stealer’s behavior — it disguises itself as legitimate software while stealing sensitive information from infected systems.
Q2 — Malware File Name
Question
Clearly identifying the name of the malware file improves communication among the SOC team. What is the file name associated with this malware?
Note: Don’t include the file extension in the name.
Analysis
On the VirusTotal main page for the sample, we can see the basic file information.
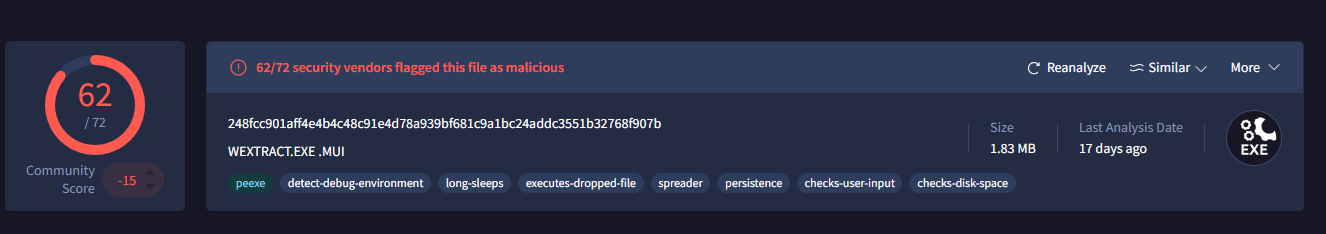 File details showing 62/72 detection rate and filename
File details showing 62/72 detection rate and filename
File Details:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Detection | 62/72 vendors flagged |
| Size | 1.83 MB (1,917,440 bytes) |
| File Type | Win32 EXE |
The file name is:
1
Wextract
Q3 — First Submission Timestamp
Question
Knowing the exact timestamp of when the malware was first observed can help prioritize response actions. Newly detected malware may require urgent containment and eradication compared to older, well-documented threats. What is the UTC timestamp of the malware’s first submission to VirusTotal?
Format: YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM
Analysis
Navigate to the Details tab in VirusTotal and scroll to the History section.
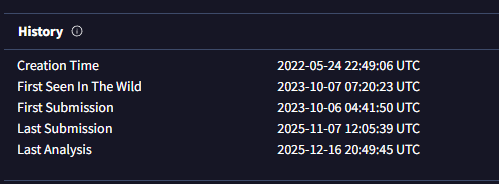 History section showing submission timeline
History section showing submission timeline
Timeline:
| Event | Timestamp (UTC) |
|---|---|
| Creation Time | 2022-05-24 22:49:06 |
| First Submission | 2023-10-06 04:41:50 |
| First Seen In Wild | 2023-10-07 07:20:23 |
| Last Submission | 2025-11-07 12:05:39 |
The first submission timestamp is:
1
2023-10-06 04:41
The malware was created in May 2022 but wasn’t submitted to VirusTotal until October 2023, suggesting it may have been used in targeted attacks before being discovered publicly.
Q4 — MITRE ATT&CK Collection Technique
Question
Understanding the techniques used by malware helps in strategic security planning. What is the MITRE ATT&CK technique ID for the malware’s data collection from the system before exfiltration?
Analysis
Navigate to the Behavior tab in VirusTotal and scroll to the MITRE ATT&CK Tactics and Techniques section. Look for techniques under the Collection tactic.
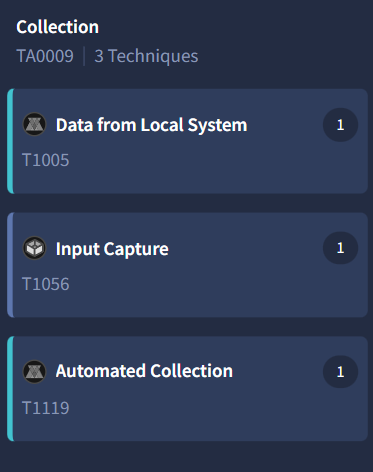 MITRE ATT&CK techniques showing Collection tactics
MITRE ATT&CK techniques showing Collection tactics
Collection Techniques Identified:
| Technique ID | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| T1005 | Data from Local System | Collects data stored on local system |
| T1056 | Input Capture | Captures user input (keylogging) |
| T1119 | Automated Collection | Automatically gathers data |
The MITRE ATT&CK technique for data collection is:
1
T1005
Why T1005?
T1005 (Data from Local System) is the primary collection method because RedLine Stealer’s core functionality targets stored data:
- Browser credentials and cookies
- Cryptocurrency wallets
- Saved passwords
- FTP/VPN credentials
- Email client data
The question asks specifically for data collection before exfiltration, and T1005 represents exactly this — gathering sensitive information from the compromised system.
Q5 — Social Media Domain Resolution
Question
Following execution, which social media-related domain names did the malware resolve via DNS queries?
Analysis
In the Behavior tab, scroll to the DNS Resolutions section to see which domains the malware contacted.
 DNS Resolutions showing facebook.com among resolved domains
DNS Resolutions showing facebook.com among resolved domains
Domains Resolved:
- business.bing.com
- connect.facebook.net (Facebook CDN)
- facebook.com ← Social media domain
- fbcdn.net (Facebook CDN)
- fbsbx.com (Facebook infrastructure)
- static.xx.fbcdn.net (Facebook CDN)
- www.facebook.com
The social media domain is:
1
facebook.com
While multiple Facebook-related domains appear (CDNs, static content servers), facebook.com is the primary social media platform domain. The malware likely resolves this to check internet connectivity or to blend in with normal user traffic.
Q6 — C2 Communication Details
Question
Once the malicious IP addresses are identified, network security devices such as firewalls can be configured to block traffic to and from these addresses. Can you provide the IP address and destination port the malware communicates with?
Analysis
In the Behavior tab, scroll to the IP Traffic section to see network connections made by the malware.
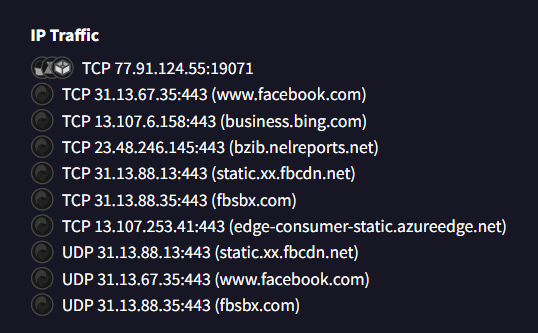 IP Traffic showing C2 server at 77.91.124.55:19071
IP Traffic showing C2 server at 77.91.124.55:19071
IP Traffic Analysis:
| Protocol | Destination | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| TCP | 77.91.124.55:19071 | Command & Control |
| TCP | 31.13.67.35:443 | www.facebook.com |
| TCP | 13.107.6.158:443 | business.bing.com |
| TCP | 31.13.88.13:443 | static.xx.fbcdn.net |
The C2 IP address and port is:
1
77.91.124.55:19071
Why is this the C2 server?
- Non-standard port 19071 — Legitimate services use standard ports (443, 80)
- Does not resolve to any legitimate domain
- First connection in the IP traffic list
- This is the attacker-controlled infrastructure receiving stolen data
IOC for Blocking:
- IP: 77.91.124.55
- Port: 19071
- Protocol: TCP
Q7 — YARA Rule Identification
Question
YARA rules are designed to identify specific malware patterns and behaviors. Using MalwareBazaar, what’s the name of the YARA rule created by “Varp0s” that detects the identified malware?
Analysis
Navigate to MalwareBazaar and search for the sample hash:
1
sha256:248fcc901aff4e4b4c48c91e4d78a939bf681c9a1bc24addc3551b32768f907b/
Scroll down to the YARA Signatures section.
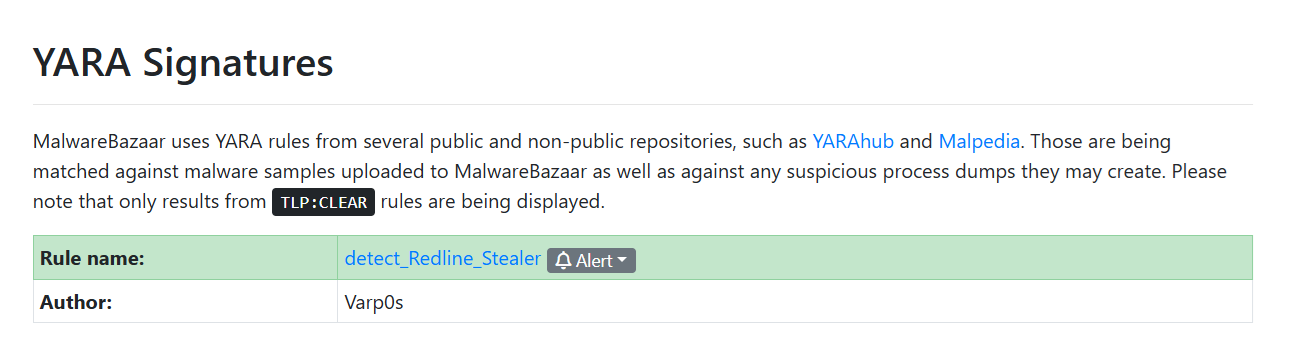 YARA Signatures section showing detect_Redline_Stealer by Varp0s
YARA Signatures section showing detect_Redline_Stealer by Varp0s
YARA Rule Details:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Rule Name | detect_Redline_Stealer |
| Author | Varp0s |
| TLP | CLEAR (publicly shareable) |
The YARA rule name is:
1
detect_Redline_Stealer
What are YARA Rules?
YARA (Yet Another Recursive Acronym) is a pattern-matching tool used to identify and classify malware based on textual or binary patterns. The detect_Redline_Stealer rule contains signatures that uniquely identify this malware family, allowing automated detection.
Q8 — Malware Alias from ThreatFox
Question
Understanding which malware families are targeting the organization helps in strategic security planning for the future and prioritizing resources based on the threat. Can you provide the different malware alias associated with the malicious IP address according to ThreatFox?
Analysis
Navigate to ThreatFox and search for the C2 IP address:
1
2
https://threatfox.abuse.ch/
Search: ioc:77.91.124.55
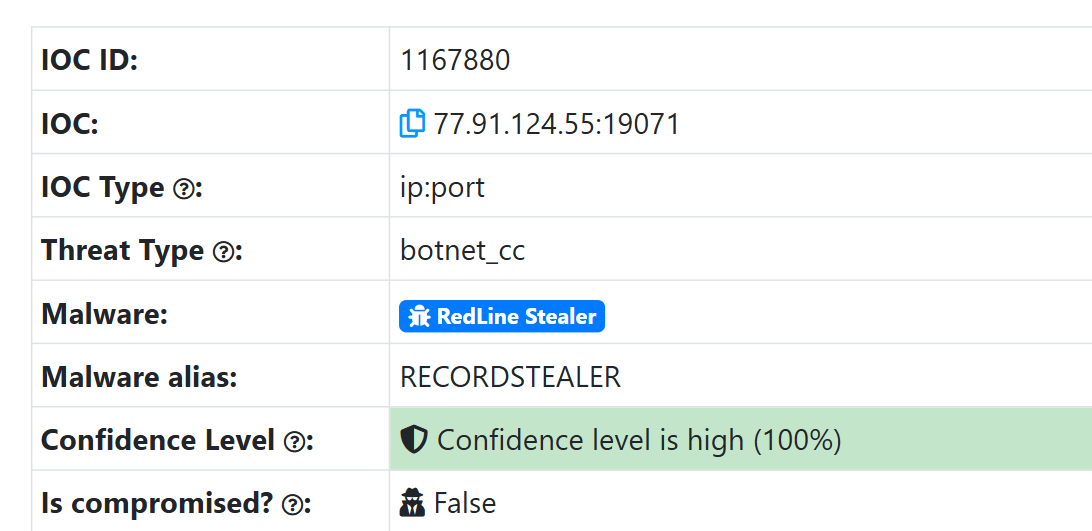 ThreatFox showing IOC with RECORDSTEALER alias
ThreatFox showing IOC with RECORDSTEALER alias
IOC Information:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| IOC | 77.91.124.55:19071 |
| IOC Type | ip:port |
| Threat Type | botnet_cc (C2) |
| Malware | RedLine Stealer |
| Malware Alias | RECORDSTEALER |
| Confidence | 100% |
The malware alias is:
1
RECORDSTEALER
Why Multiple Names?
Malware families often have aliases assigned by different vendors:
- RedLine Stealer — Common industry name
- RECORDSTEALER — Alias in threat intelligence databases
This helps correlate threats across different security platforms and vendor reports.
Q9 — Privilege Escalation DLL
Question
By identifying the malware’s imported DLLs, we can configure security tools to monitor for the loading or unusual usage of these specific DLLs. Can you provide the DLL utilized by the malware for privilege escalation?
Analysis
In the Behavior tab on VirusTotal, scroll to the Modules loaded section.
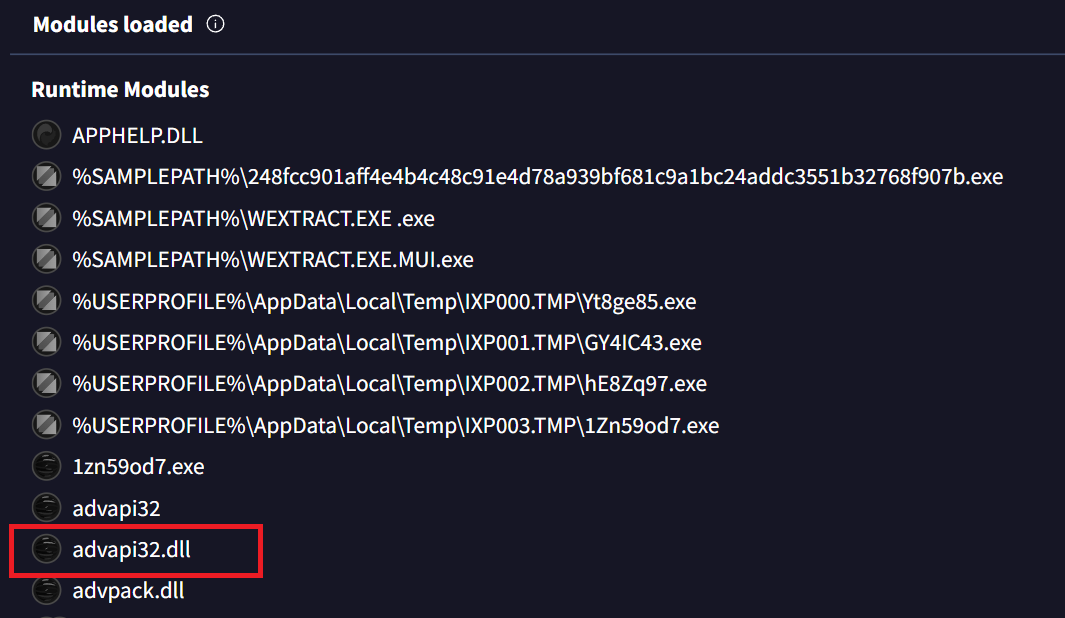 Runtime Modules showing advapi32.dll for privilege escalation
Runtime Modules showing advapi32.dll for privilege escalation
Runtime Modules Loaded:
- APPHELP.DLL
- advapi32.dll ← Privilege escalation DLL
- advpack.dll
- Various dropped executables in
%TEMP%\IXP00X.TMP\
The privilege escalation DLL is:
1
advapi32.dll
What is advapi32.dll?
advapi32.dll (Advanced Windows 32 Base API) is a Windows system library providing access to:
- Security and privilege management
- Registry manipulation
- Service management
- User account control
- Token manipulation
Why is this used for privilege escalation?
This DLL contains critical Windows API functions commonly abused by malware:
| Function | Purpose |
|---|---|
AdjustTokenPrivileges() | Modify security tokens |
OpenProcessToken() | Access process security tokens |
LookupPrivilegeValue() | Query privilege information |
ImpersonateLoggedOnUser() | Impersonate user accounts |
By monitoring unusual loading or API calls to advapi32.dll, security tools can detect privilege escalation attempts.
Conclusion
This investigation successfully identified a RedLine Stealer sample (alias: RECORDSTEALER) communicating with a C2 server at 77.91.124.55:19071.
Summary of Findings
| Question | Finding |
|---|---|
| Q1 | Microsoft category: Trojan |
| Q2 | File name: Wextract |
| Q3 | First submission: 2023-10-06 04:41 |
| Q4 | MITRE ATT&CK Collection: T1005 |
| Q5 | Social media domain: facebook.com |
| Q6 | C2 IP:Port: 77.91.124.55:19071 |
| Q7 | YARA rule: detect_Redline_Stealer |
| Q8 | Malware alias: RECORDSTEALER |
| Q9 | Privilege escalation DLL: advapi32.dll |
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
File Indicators:
| Type | Value |
|---|---|
| SHA256 | 248fcc901aff4e4b4c48c91e4d78a939bf681c9a1bc24addc3551b32768f907b |
| MD5 | 18cbe55c3b28754916f1cbf4dfc95cf9 |
| SHA-1 | 7ccfb7678c34d6a2bedc040da04e2b5201be453b |
Network Indicators:
| Type | Value |
|---|---|
| C2 IP | 77.91.124.55 |
| C2 Port | 19071 |
| Protocol | TCP |
Through open-source threat intelligence platforms (VirusTotal, MalwareBazaar, ThreatFox), we gathered comprehensive IOCs for the SOC and Incident Response teams to detect, block, and hunt for this threat across the organization.